Shoulder bursitis
What is shoulder bursitis?
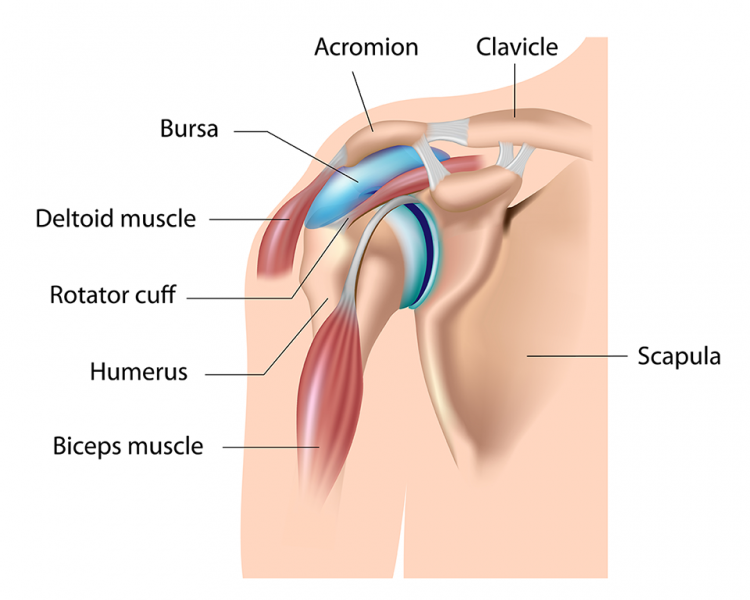
The shoulder contains numerous structures (muscle, bone, ligaments, tendons and bursae) that work closely together to allow optimum functioning. Within each shoulder is two purse-like sacs that contain fluid: the sub-acromial and sub-deltoid bursae. These both help to reduce friction over adjacent surfaces (i.e. muscle on muscle, bone to muscle) [1]. When irritated, this leads to a thickening of the bursa causing a painful condition known as bursitis [2].
This is considered an active warning sign that the surrounding structures have undergone repeated trauma from overuse or have been involved in a single incident (i.e. collision) [1, 2, 3]. Poor body mechanics can also be a contributing factor to the onset of bursitis [2]. It has been commonly associated with chronic shoulder pain, rotator cuff tears and degenerative tendinitis of the rotator cuff [3].
Presentation?
Tender, swelling, painful when directly palpated
Pain when lying on shoulder
Pain when lifting shoulder
Limited range in all directions due to pain
Gradual onset of pain and limitations
Difficultly doing overhead activities
Complications – Septic Shoulder
Is a rare condition in which the bursa becomes infected. Sepsis is caused in the bursa because of direct contact piercing through the skin in the form of isotretinoin therapy and corticosteroid injections [4]. Individuals will feel the same symptoms as listed above, however, they may also become feverish, tired and sick. The shoulder may appear red and radiate heat [2, 4, 5]. Treatment should be sought from a medical practitioner to provide antibiotics to prevent the spread of the infection [2, 4, 5].
How can Physiotherapy help?
Perform a thorough postural and movement examination of the upper body to provide education and understanding into condition.
Provide tailored strategies and modifications to correct improper biomechanics of the shoulder, i.e. taping, ergonomic assessment.
Design a personalised exercise program tailored to resolving muscle imbalances that would otherwise cause shoulder bursitis.
Assist with improving range and pain management strategies.
Provide education on self-management techniques.
If you have any questions regarding your shoulder pain, please give us a call at (02) 8411 2050. At Thornleigh Performance Physiotherapy, we can give you an accurate diagnosis and treatment, to help you get back in action as soon as possible. We are conveniently located near Beecroft, Cherrybrook, Hornsby, Normanhurst, Pennant Hills, Waitara, Wahroonga, Westleigh, West Pennant Hills, and West Pymble.
References
Lennard, T. (2011). Pain procedures in clinical practice / Ted A. Lennard ... [et al.]. (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders
What is shoulder (subacromial) bursitis? (2013). https://www.arthritis-health.com/types/bursitis/shoulder-subacromial-bursitis
Santavirta, S., Konttinen, Y., Antti-Poika, T., & Nordström, I. (1992). Inflammation of the subacromial bursa in chronic shoulder pain. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery,111(6), 336-340.
Drezner, J., & Sennett, B. (2004). Subacromial/subdeltoid septic bursitis associated with isotretinoin therapy and corticosteroid injection. The Journal of the American Board of Family Practice, 17(4), 299-302.
Khan, H., & Al-Tawil, K. (2013). Spontaneous Isolated Infection of the Subacromial Bursa. Case Reports in Orthopedics, 2013, 3